Silent Sinus Syndrome Current Opinion
Silent sinus syndrome current opinion. The medical history is often noncontributory. The pathophysiology involves a negative pressure phenomenon within the sinus leading to inward bowing of the sinus walls. To challenge current exclusion criteria of antecedent facial trauma we have identified all published cases of posttraumatic SSS in English literature including a new representative case from our institution.
Treatment consists of correction of the maxillary sinus atelectasis and the orbital defects. Silent sinus syndrome is a rare disorder but it is probably underdiagnosed because of a lack of recognition 1. Treatment consists of correction of the maxillary sinus atelectasis and the orbital defects.
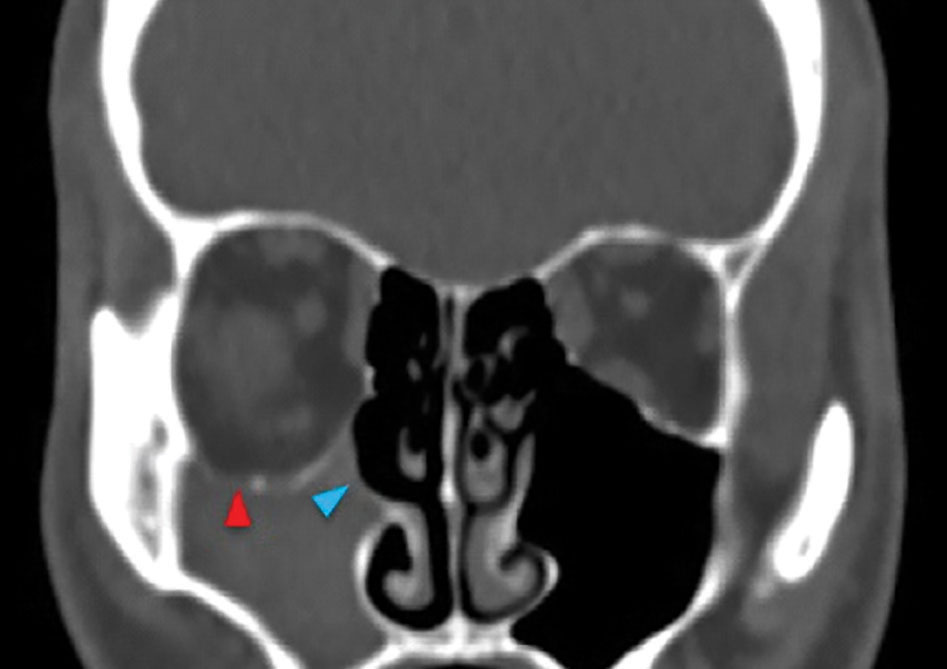
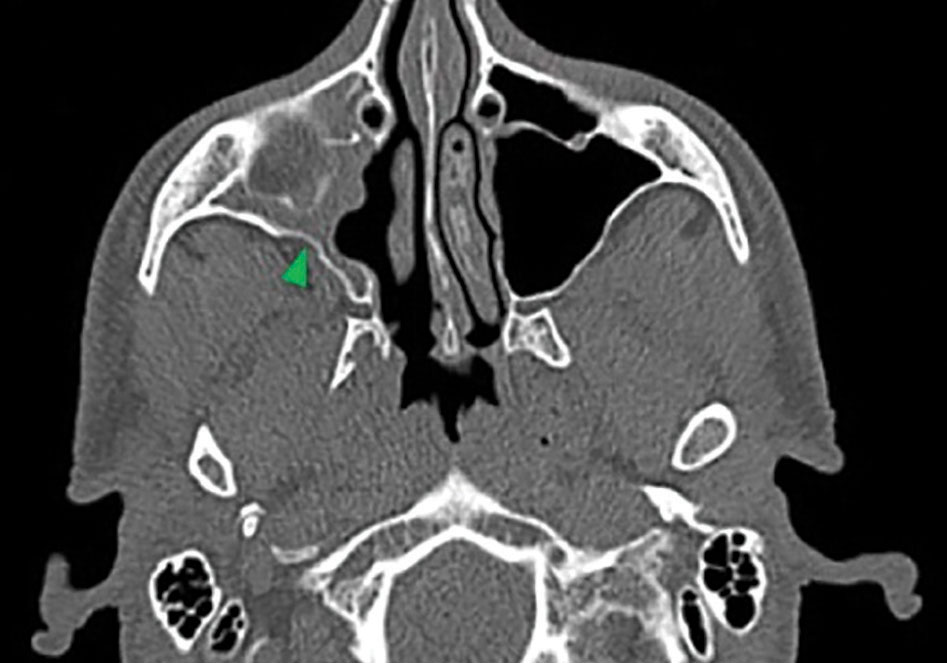
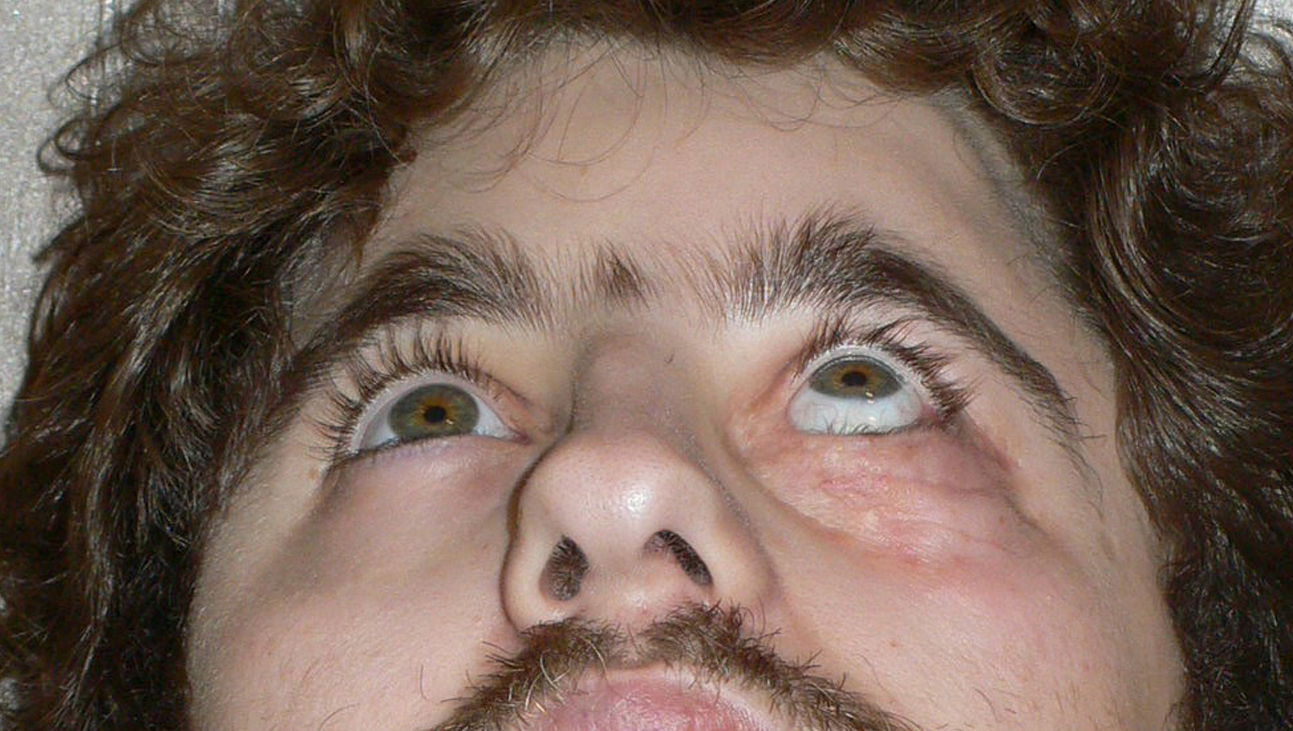
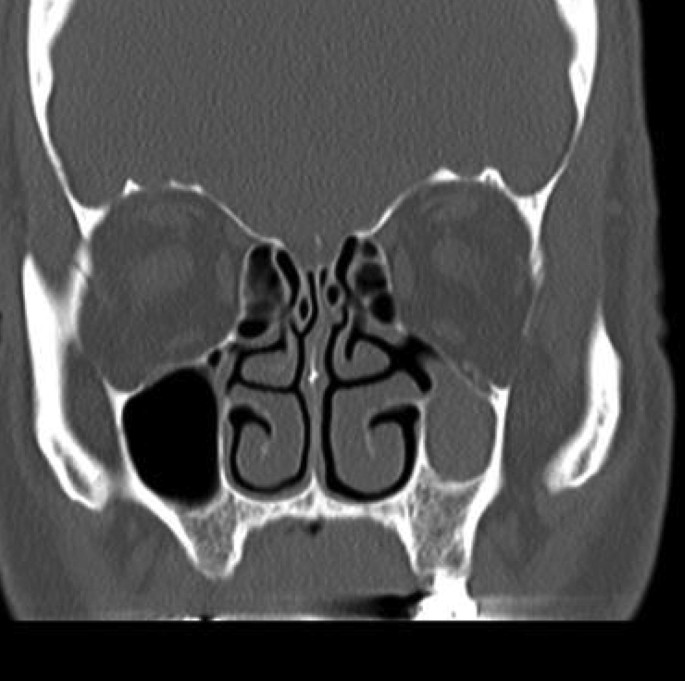
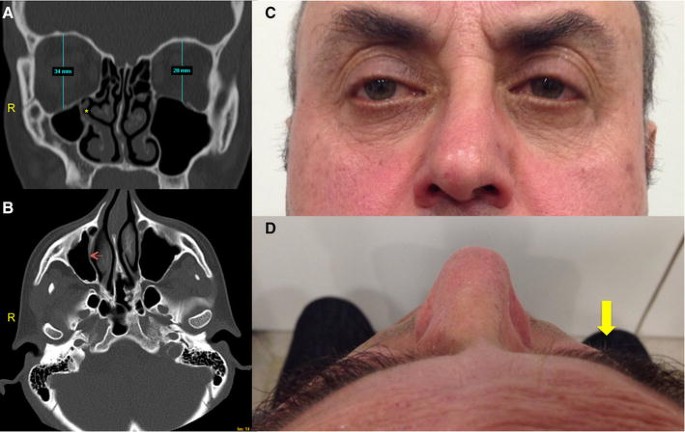
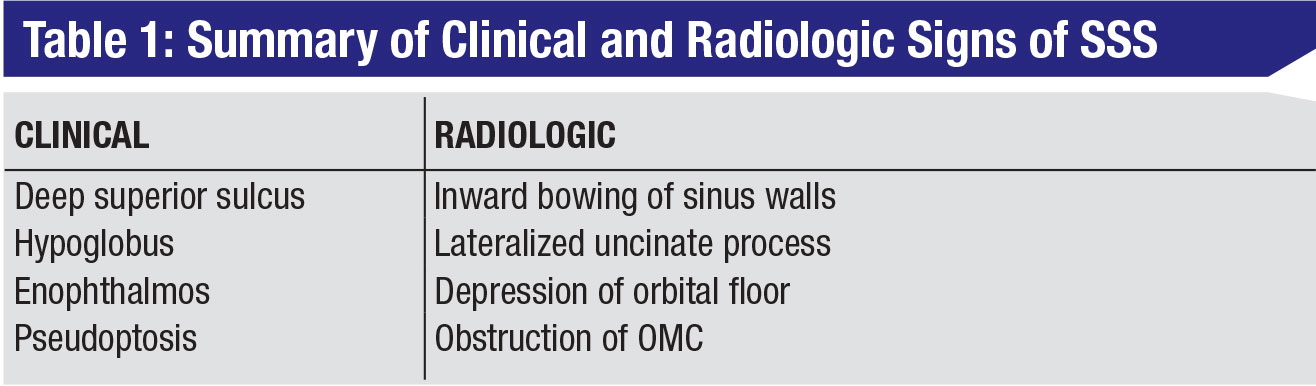
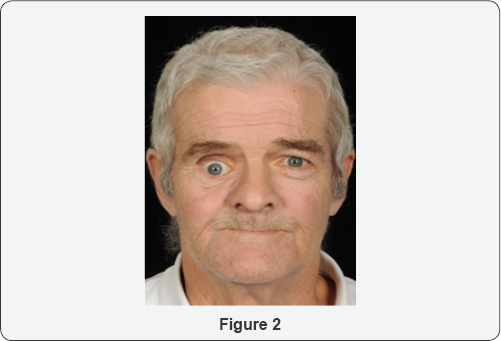
The visual sign of silent sinus syndrome is the asymmetry of the face and the asymmetry of face may lead to many other problems like diplopia. Recent findings Silent sinus syndrome lies on a spectrum of other forms of sinus-related orbitopathy. Radiographic features of disease include an opacified and hypoplastic sinus a lateralized uncinate process depression of the orbital.
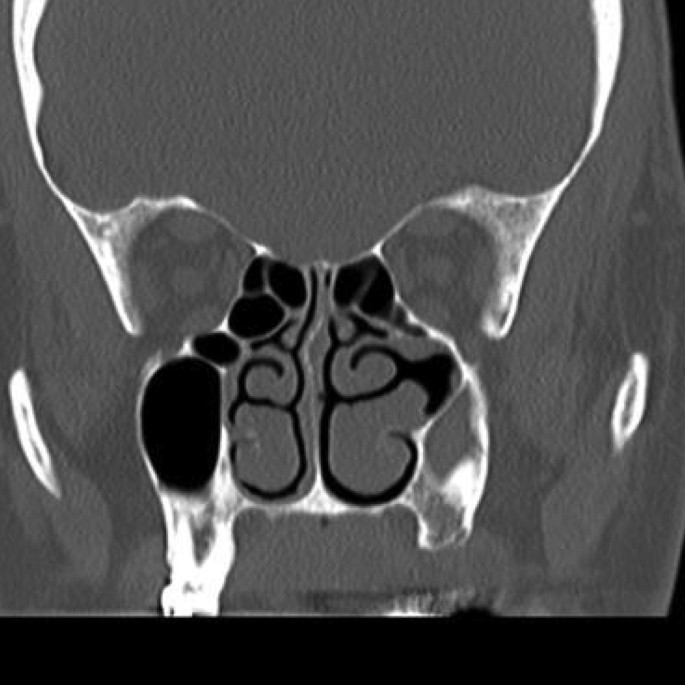
Vely rare clinical entity. Is this Silent Sinus Syndrome. The silent sinus syndrome is a spontaneous unilateral maxillary atelectasis with complete or partial opacification of the sinus.
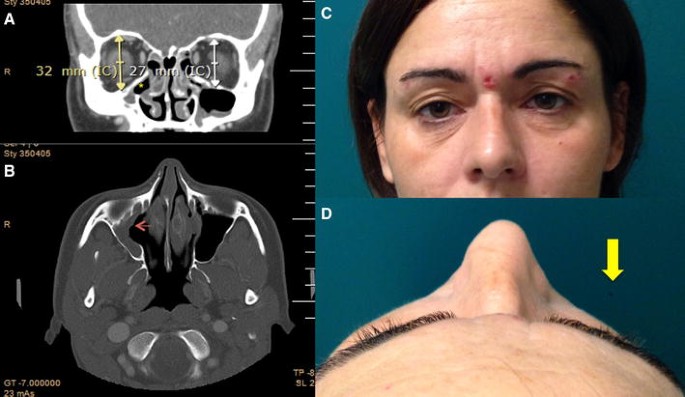
The patient may present with unilateral ptosis or retraction a deep superior sulcus or orbital asymmetry. Silent sinus syndrome is more common in patients in their 30s and 40s ranging from 19 to 82 years mean 39 without gender or laterality bias. It mainly presents as unilateral enophthalmos in younger people and has very characteristic clinical and radiologic signs.
The first case of maxillary sinus opacification and atelectasis was reported by Montgomery in 1964 It was not until 30 years later however that the term silent sinus syndrome was attributed to this phenomenon Patients typically present with unilateral painless enophthalmos and hypoglobus progressing over a period of several months. The silent sinus syndrome is characterized by painless enophthalmos associated with involution of the maxillary sinus after infundibular occlusion 12345678910. The hypoventilation over time results in resorption of.
Silent sinus syndrome is a rare condition that can pose a diagnostic challenge. One such disease process silent sinus syndrome is a progressive condition in which maxillary sinus pathology causes inferior displacement of the orbital floor resulting in enophthalmos and hypoglobus.
When looking at all the pictures on google the symptoms its all matching.
Silent sinus syndrome is rare and multiple findings are needed for the diagnosis. The hypoventilation over time results in resorption of. Diplopia is seen in about 28 to 65 of cases regarding silent sinus syndrome. Silent sinus syndrome is more common in patients in their 30s and 40s ranging from 19 to 82 years mean 39 without gender or laterality bias. These include enophthalmos or hypoglobus in the absence of clinically evident sinonasal inflammatory disease. The first case of maxillary sinus opacification and atelectasis was reported by Montgomery in 1964 It was not until 30 years later however that the term silent sinus syndrome was attributed to this phenomenon Patients typically present with unilateral painless enophthalmos and hypoglobus progressing over a period of several months. 5 The proposed mechanism for the development of silent sinus syndrome is a hypoventilated maxillary sinus from an obstructed ostiomeatal complex. The silent sinus syndrome is a spontaneous unilateral maxillary atelectasis with complete or partial opacification of the sinus. The silent sinus syndrome is a rare clinical entity of spontaneous enophthalmos and hypoglobus caused by an alteration of the normal orbital architecture and function from maxillary sinus collapse in the setting of chronic sinusitis.
When looking at all the pictures on google the symptoms its all matching. Ocular motility limitation also occur and sometimes reported along with hypo Globus. Silent sinus syndrome is more common in patients in their 30s and 40s ranging from 19 to 82 years mean 39 without gender or laterality bias. Silent sinus syndrome is usually diagnosed in patients in their 30s and 40s with a mean age of 39 and a range of 19 to 82 11. Radiographic features of disease include an opacified and hypoplastic sinus a lateralized uncinate process depression of the orbital. Uncommon presentations and descriptions of sinus involvement other than the maxillary sinus add to the variability of presentation. These include enophthalmos or hypoglobus in the absence of clinically evident sinonasal inflammatory disease.































Post a Comment for "Silent Sinus Syndrome Current Opinion"