Fap Vs Lynch Syndrome
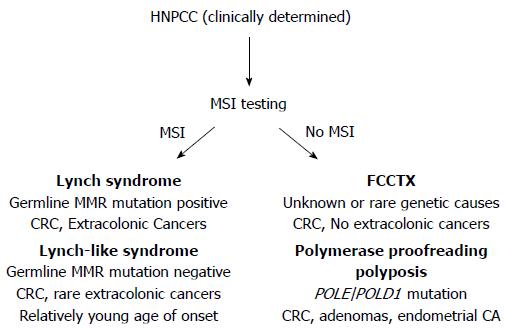
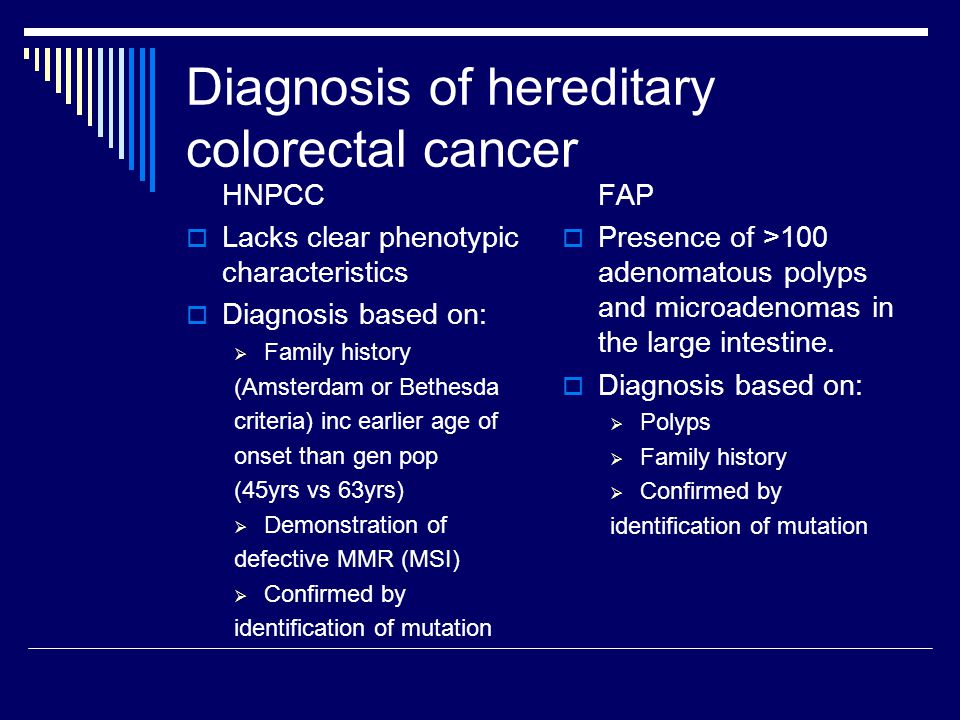
Fap vs lynch syndrome. Affected individuals develop a small number of adenomas that can rapidly progress to colorectal cancer CRC resulting in a considerably earlier symptom onset compared to. HNPCC may technically present with polyps so the non-polyposis part of HNPCC is really a relative lack of polyps -- HNPCC has much fewer polyps than does FAP. Lynch syndrome or hereditary nonpolyposis colon cancer HNPCC is a familial cancer syndrome caused by an autosomal dominant mutation in DNA mismatch repair MMR genes.
Patients with a differential diagnosis of attenuated FAP vs MAP vs Lynch syndrome. The 2 most common types of brain tumors in Turcot syndrome are. In this article Dr.
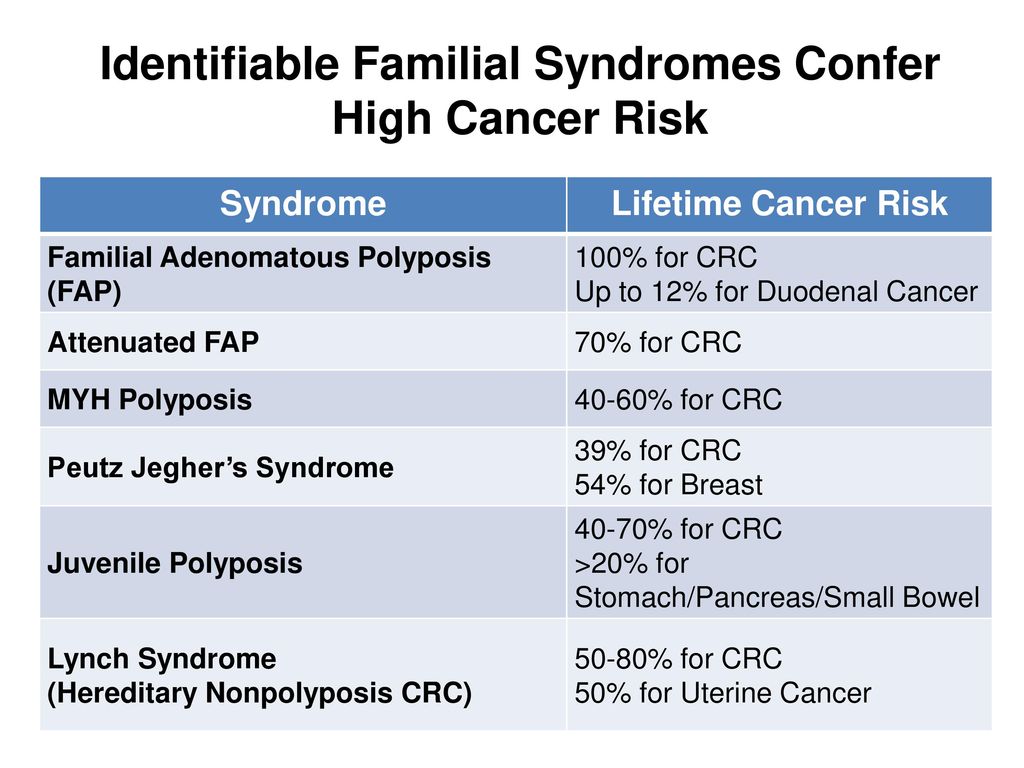
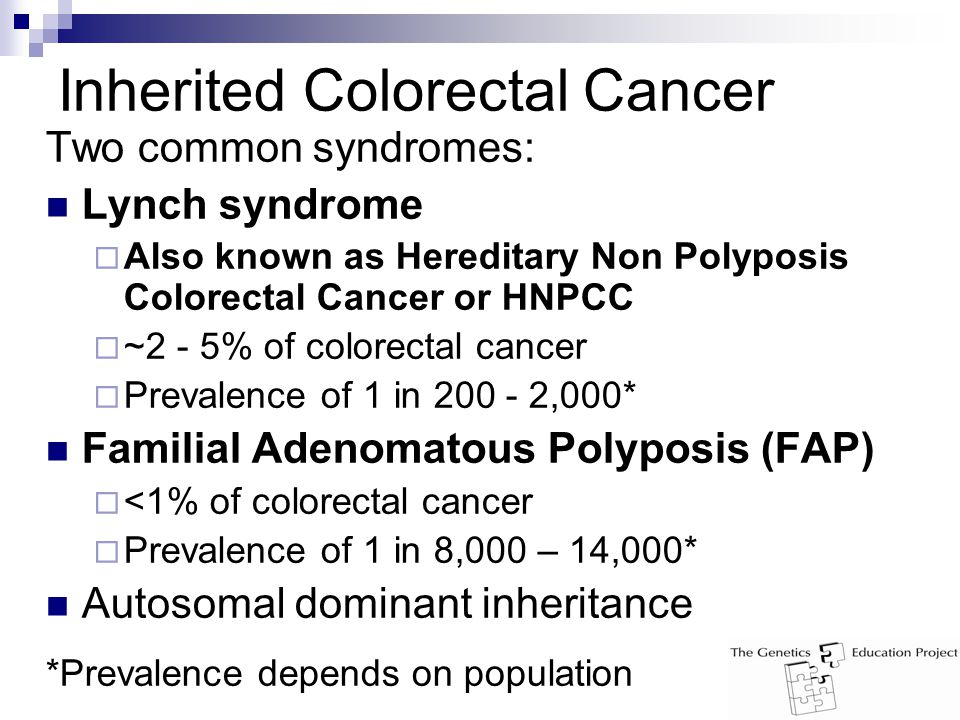
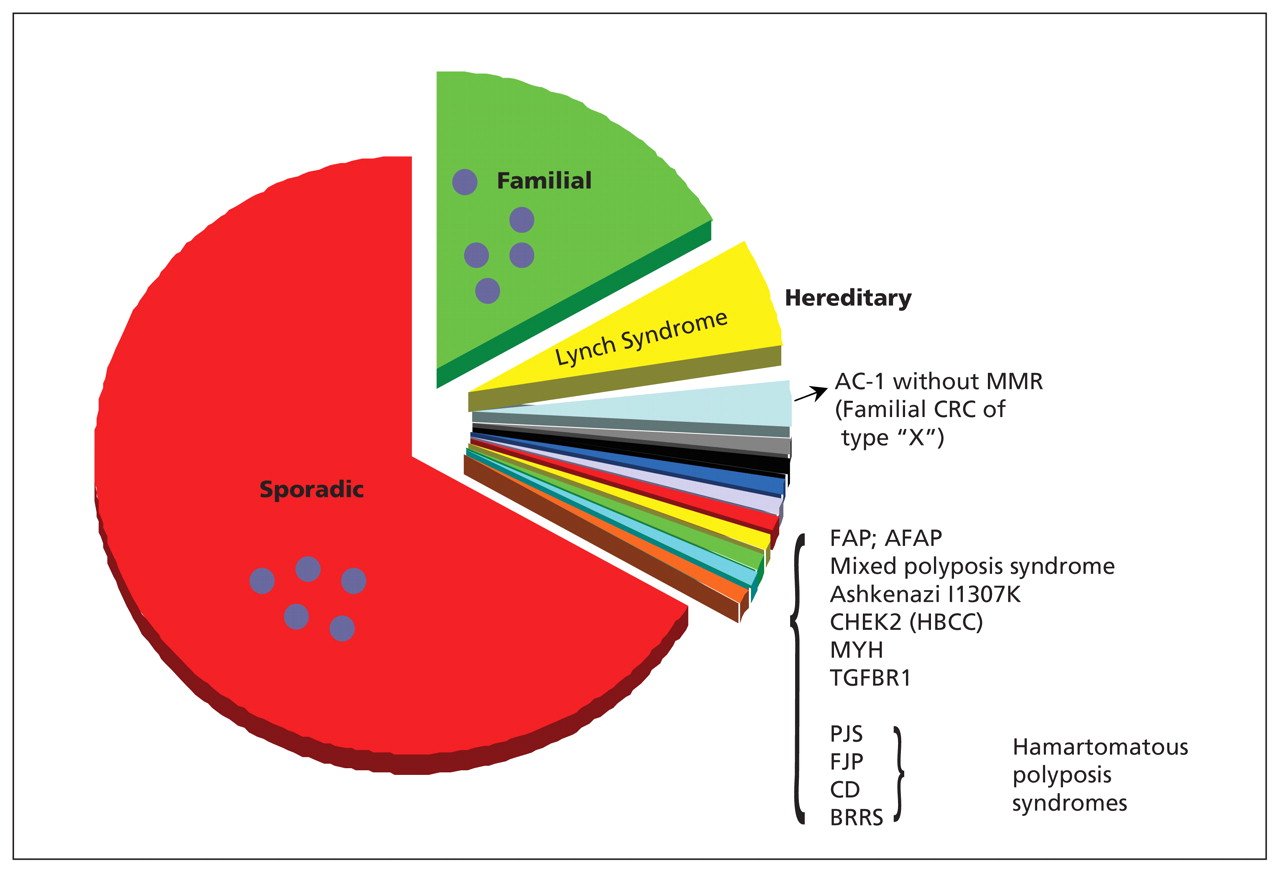
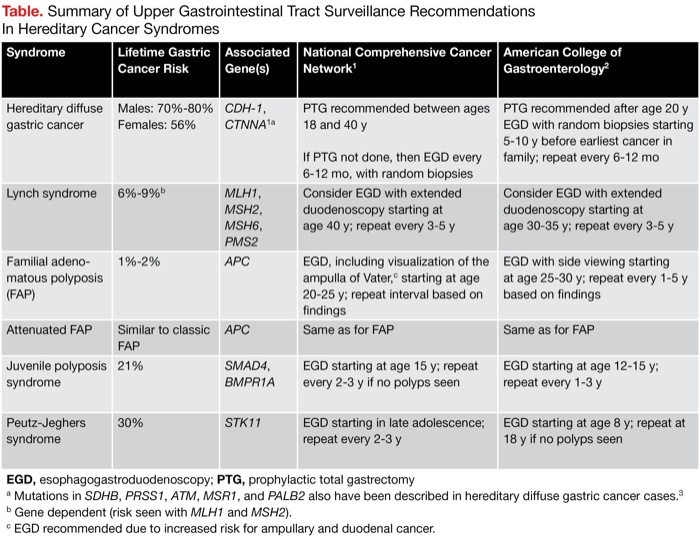
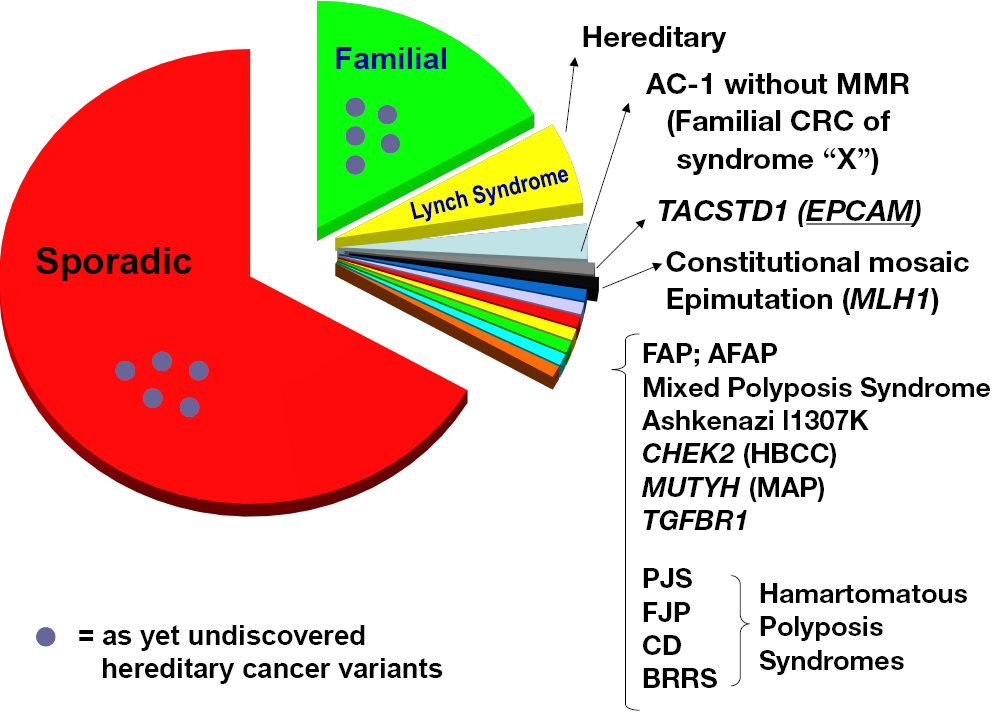
Samadder shares information about Lynch syndrome LS familial adenomatous polyposis FAP and attenuated FAP AFAP to provide clinicians with tools to understand the genetic bases of these conditions and the appropriate diagnosis and management. Individuals with Lynch syndrome have an increased risk for other cancers including ovary stomach small intestine urinary tractbladderkidney bile duct pancreas sebaceous gland and. Two major autosomal dominant forms of heritable CRC are familial adenomatous polyposis FAP and Lynch syndrome also known as hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer.
Whether testing begins with APC variants. FAP typically develops by age 16 years and can be identified by the appearance of hundreds to. Family history of early onset of colorectal polyps.
Patients with a differential diagnosis of FAP vs. This type of brain tumor is a very aggressive form of astrocytoma that is commonly found in families who have features of Lynch syndrome. Personal or family history of duodenal adenoma common carcinoma may occur.
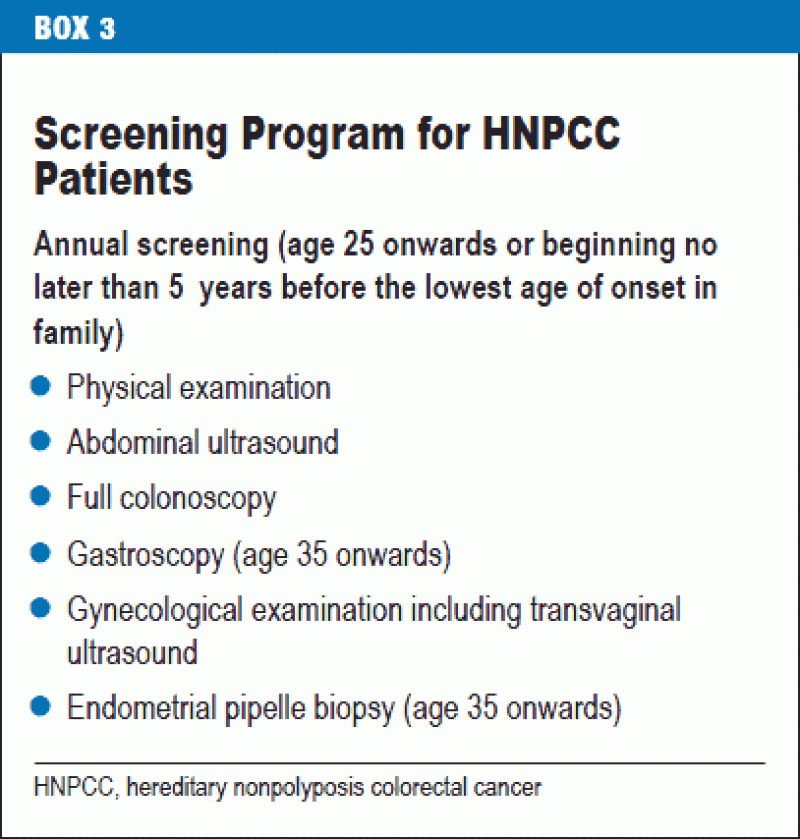
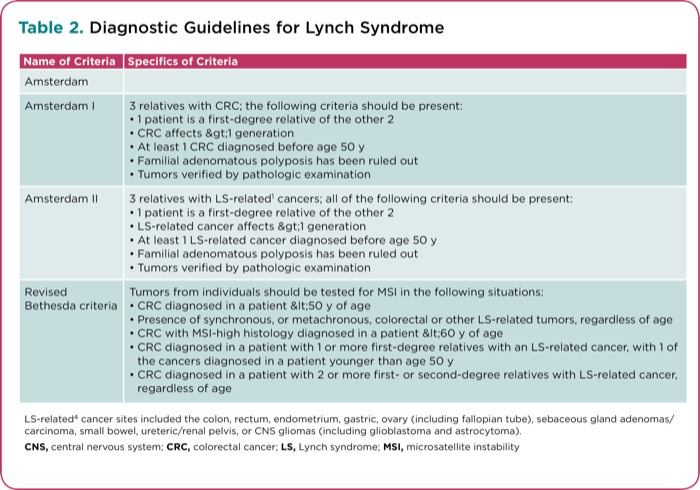
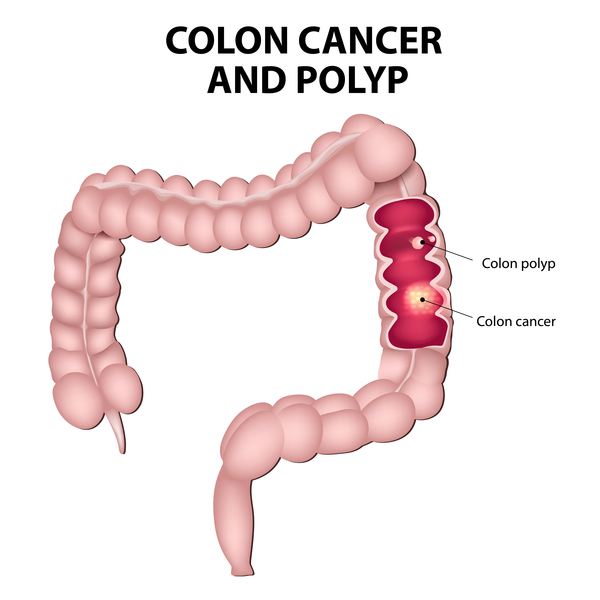
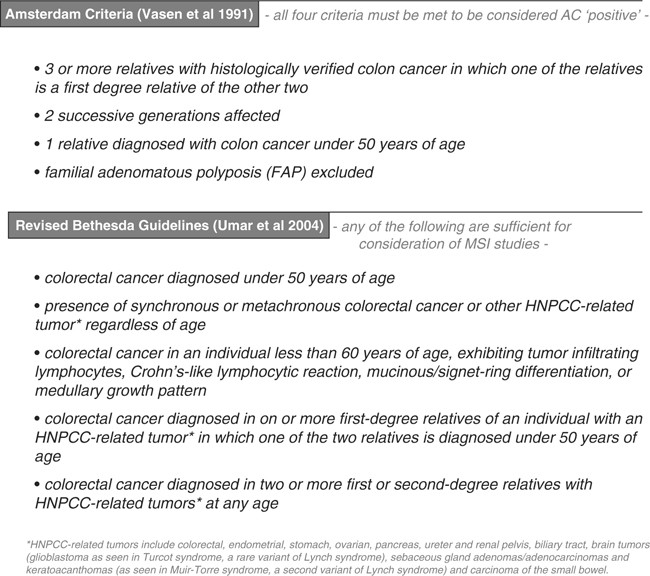
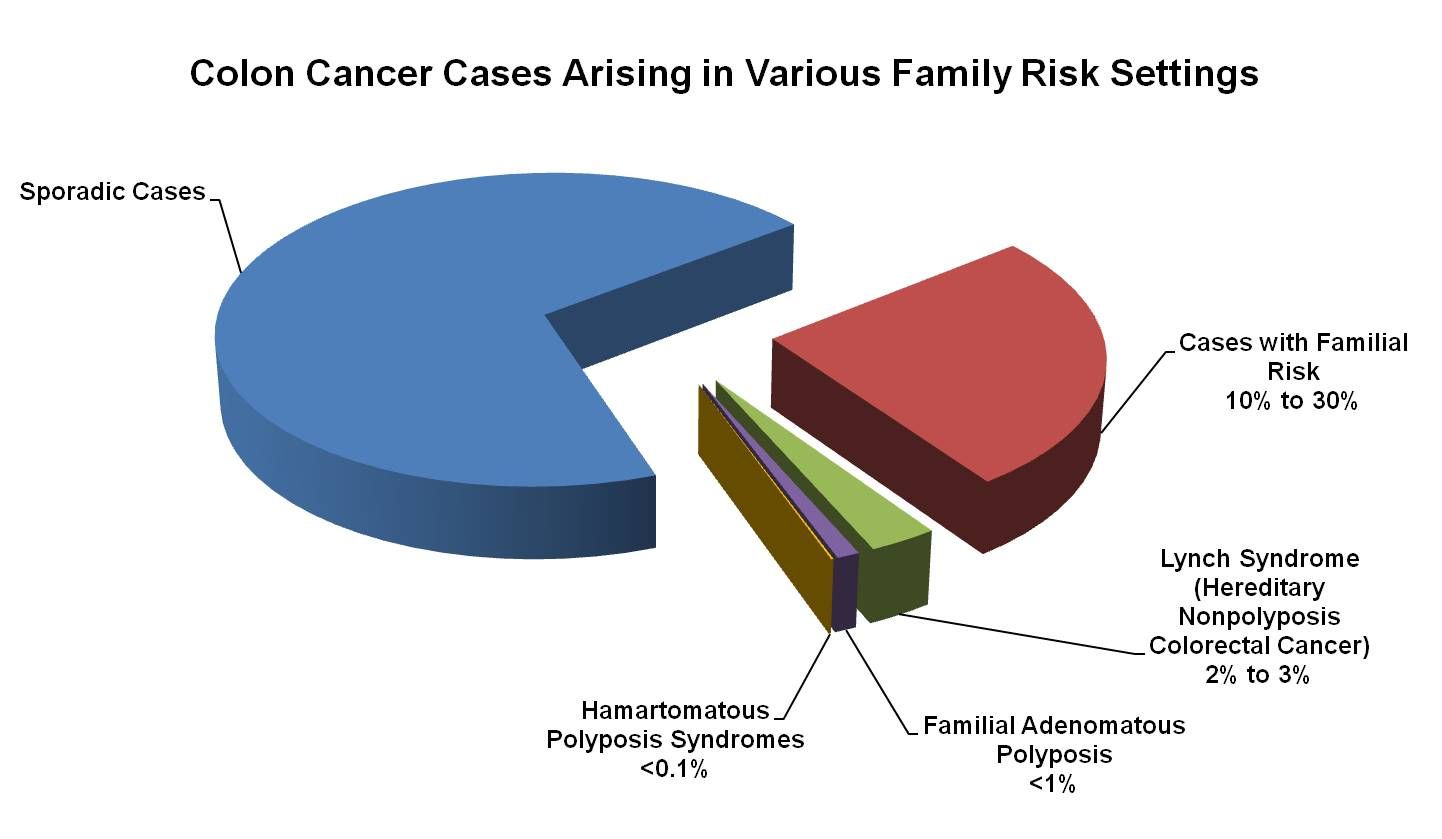
Also called hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer HNPCC this inherited disorder increases the risk of colon cancer and uterine cancer. An estimated 2-4 of all colorectal cancers are due to Lynch syndrome. Patients with a differential diagnosis of attenuated FAP vs.
1-3 Familial adenomatous polyposis FAP. Lynch syndrome has been implicated in some endometrial cancers as well.
Familial adenomatous polyposis and associated variants.
Lynch syndrome is an inherited disorder that results in a higher predisposition to CRC and other malignancies including endometrial and gastric cancer. Samadder shares information about Lynch syndrome LS familial adenomatous polyposis FAP and attenuated FAP AFAP to provide clinicians with tools to understand the genetic bases of these conditions and the appropriate diagnosis and management. Gardner syndrome is an autosomal dominant form of polyposis characterized by the presence of multiple polyps in the colon together with tumors outside the colon. Personal or family history of duodenal adenoma common carcinoma may occur. Lynch syndrome is suspected in patients with colorectal cancer or endometrial cancer D. MYH-associated polyposis syndrome is a recently characterized. The extracolonic tumors may. Hundreds to thousands of polyps are an obvious indication of the syndrome and therefore genetic testing is not so critical to make the diagnosis. Patients with a differential diagnosis of attenuated FAP vs MAP vs Lynch syndrome.
MYH-associated polyposis syndrome is a recently characterized. Familial adenomatous polyposis and associated variants. Lynch syndrome has been implicated in some endometrial cancers as well. Affected individuals develop a small number of adenomas that can rapidly progress to colorectal cancer CRC resulting in a considerably earlier symptom onset compared to. MYH-associated polyposis syndrome is a recently characterized. The type of brain tumor generally depends on whether the Turcot syndrome is more similar to Lynch syndrome or more similar to FAP. Patients with a differential diagnosis of attenuated FAP vs MAP vs Lynch syndrome.



























Post a Comment for "Fap Vs Lynch Syndrome"