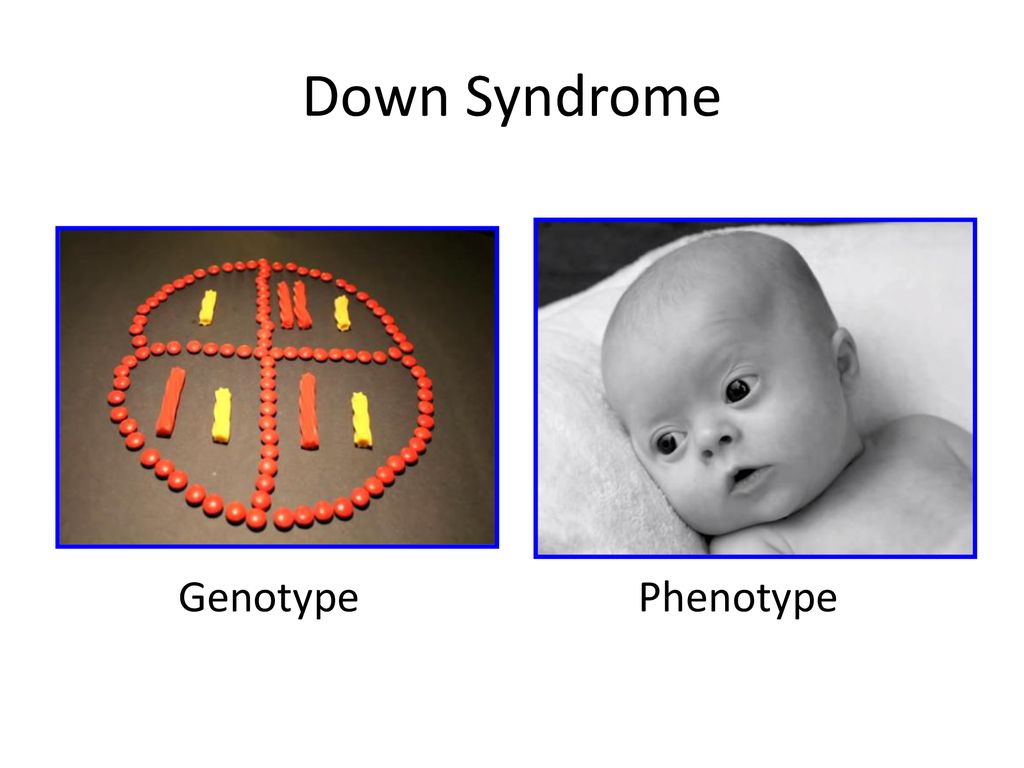
Phenotype Of Down Syndrome
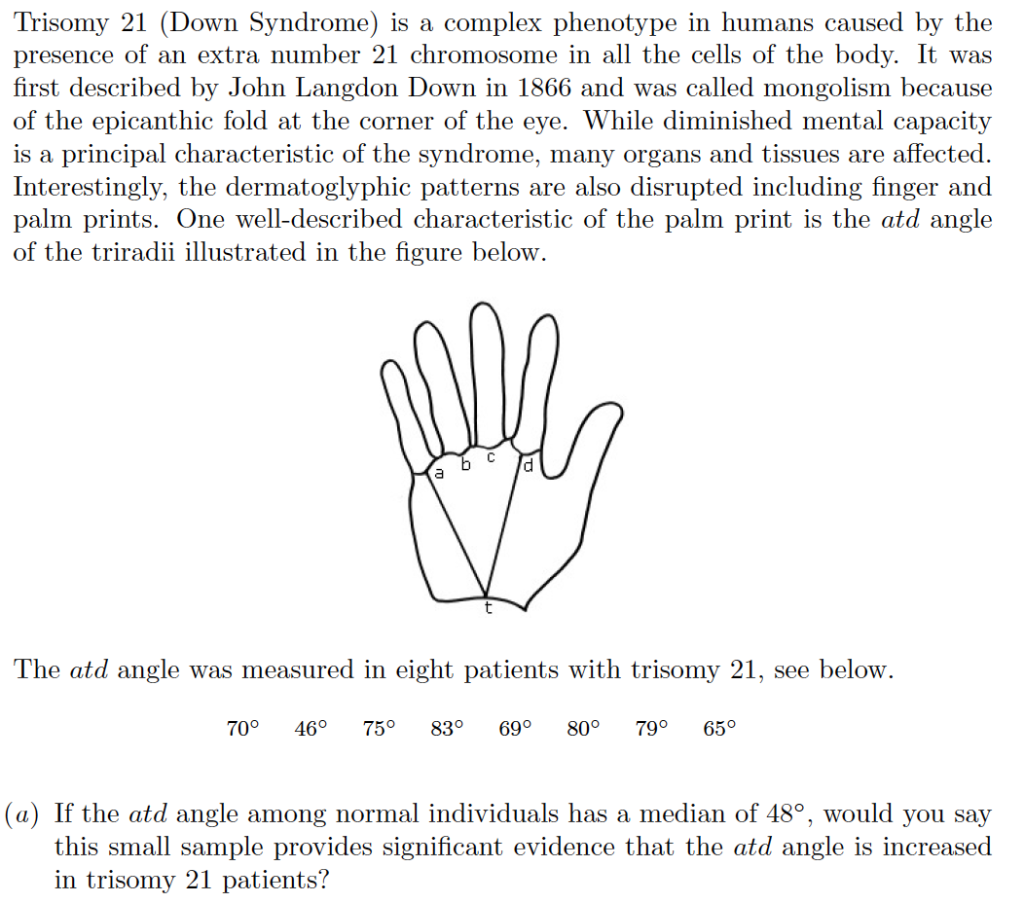
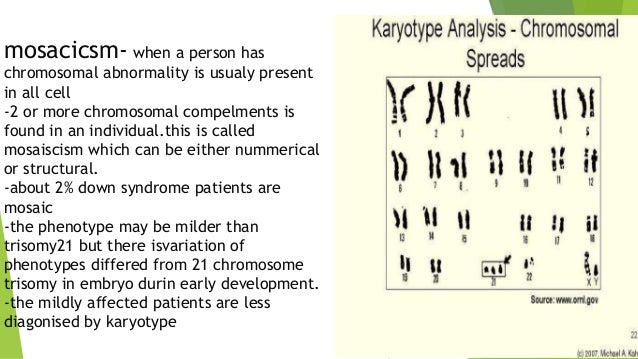
Phenotype of down syndrome. A number sign is used with this entry because 4 known genetic mechanisms can cause Angelman syndrome AS. The phenotype of persons having mosaicism for trisomy 21Down syndrome reflects the percentage of trisomic cells present in different tissues. Am J Med Genet A.
GeneReviews an international point-of-care resource for busy clinicians provides clinically relevant and medically actionable information for inherited conditions in a standardized journal-style format covering diagnosis management and genetic counseling for patients and their families. A New Mutation Identified by. Learn about Gregor Mendel his seminal experiments and the basic foundations of genetics in this videoPicture of Mendel by Hugo Iltis.
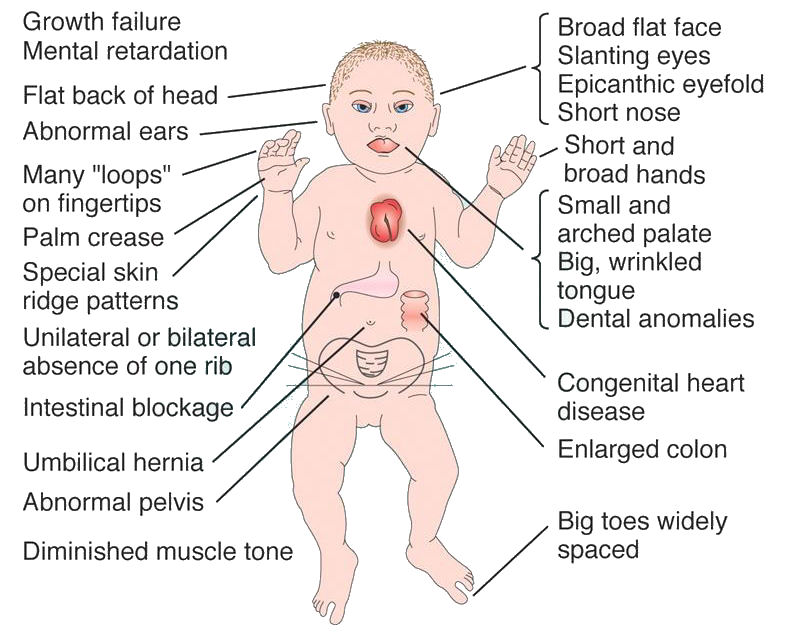
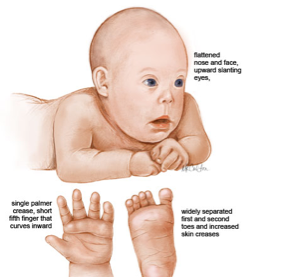
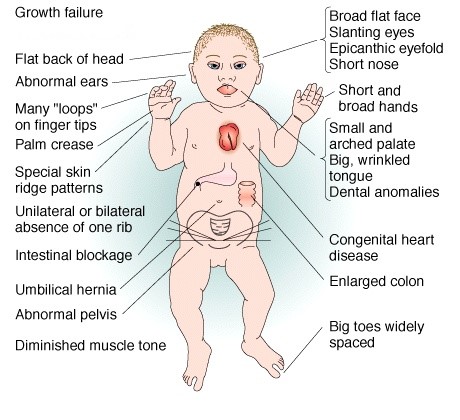
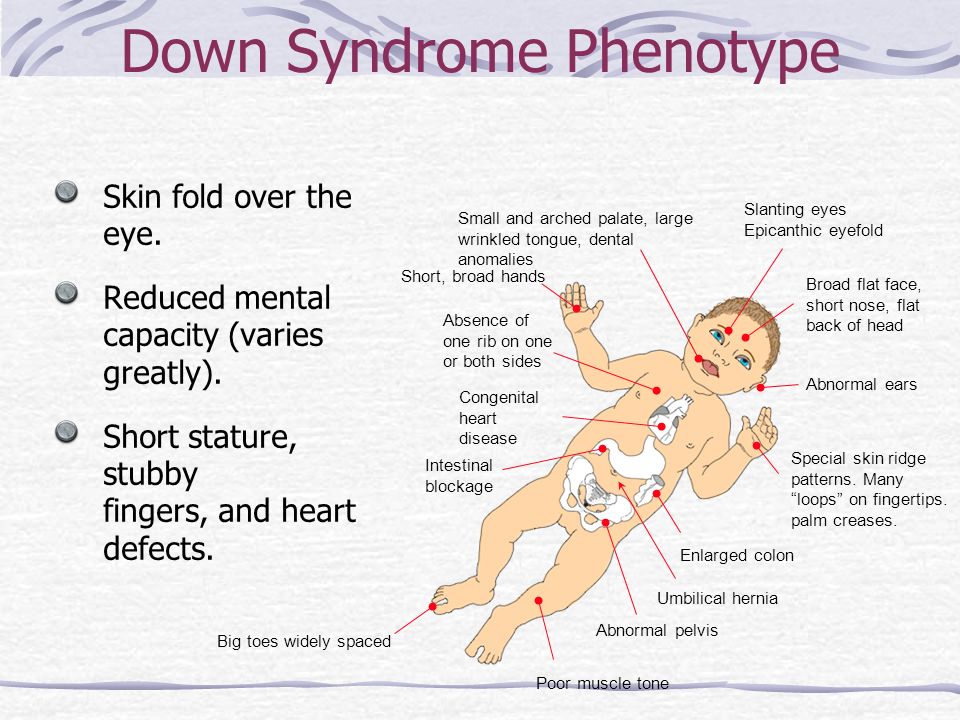
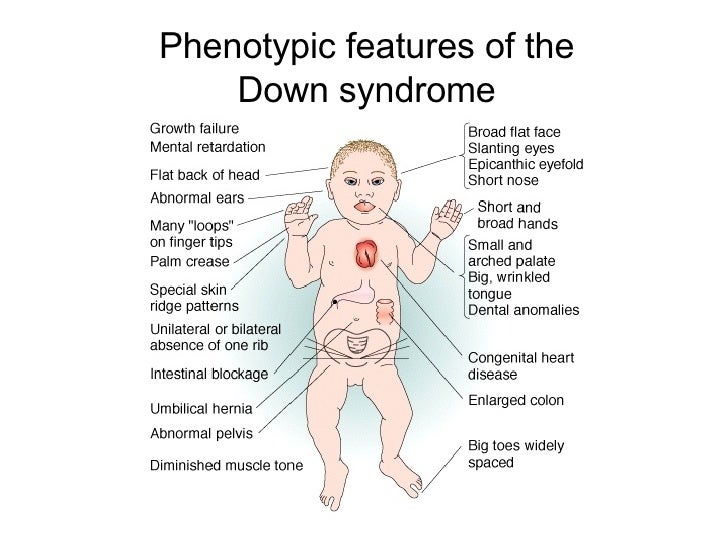
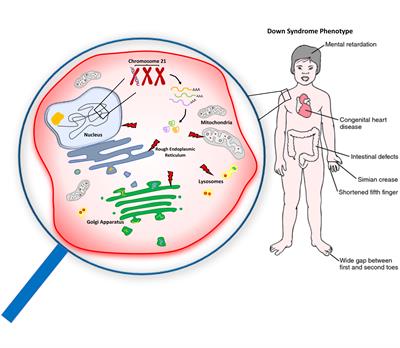
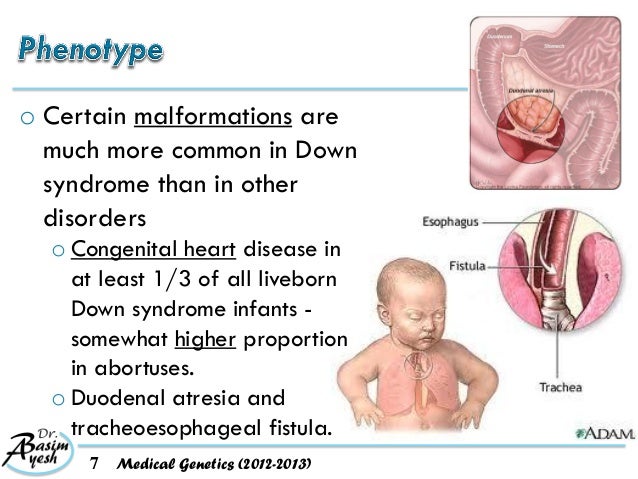
People with Down syndrome may also be born with various health concerns such as heart defects or digestive abnormalities as. Less commonly Down syndrome occurs when part of chromosome 21 becomes attached translocated to another chromosome during the formation of reproductive cells eggs and sperm in a parent or very early in fetal development. In patients with Down syndrome there is great variability in phenotype.
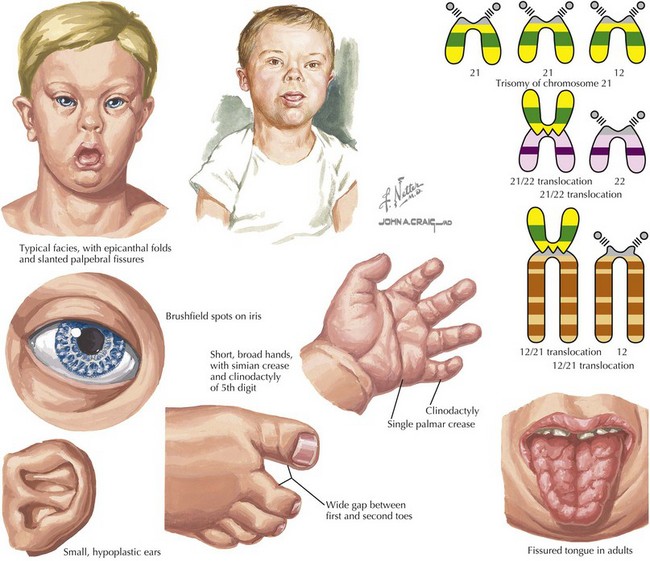
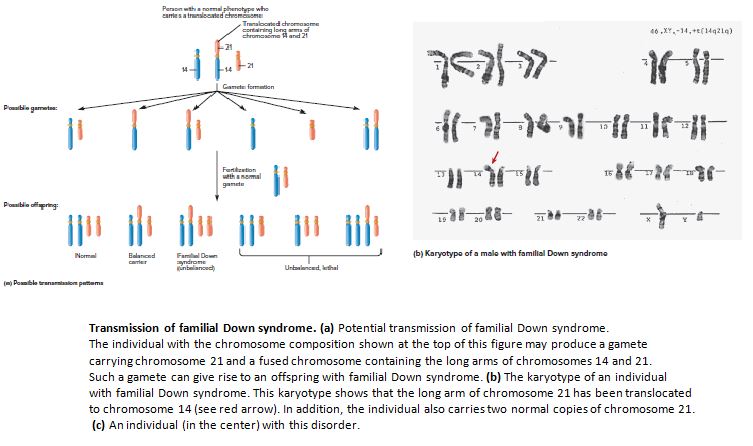
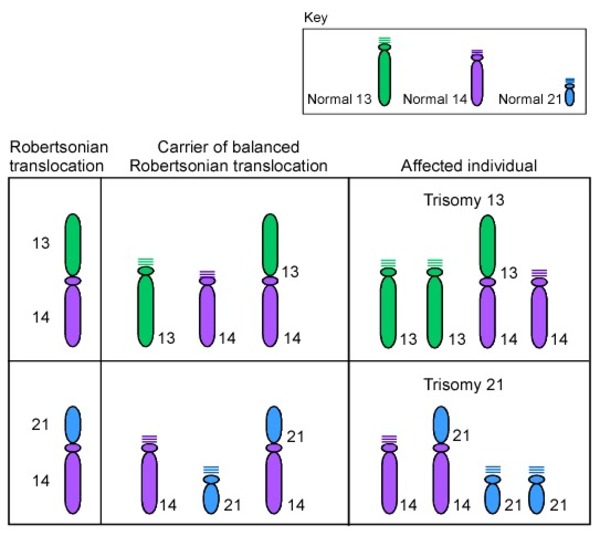
The first clinical case of UPD was reported in 1988 and involved a girl with cystic fibrosis and short stature who carried two copies of maternal chromosome 7. People with this condition also have delayed development and intellectual disability usually ranging from moderate to severeHeart defects occur in most people with cardiofaciocutaneous syndrome. Proximately 3 to 4 of persons with the Down syndrome phenotype the extra chromosomal material is the result of an unbalanced trans-location between chromosome 21 and another acrocentric chromo-someusuallychromosome14Approximatelythree-quartersofthese MarilynJ.
In approximately 3 to 4 of persons with the Down syndrome phenotype the extra chromosomal material is the result of an unbalanced translocation between chromosome 21 and another acrocentric chromosome usually chromosome 14. As a result recessive traits can be expressed. Individuals with Down syndrome DS commonly possess unique neurocognitive and neurobehavioral profiles that emerge within specific developmental periods.
The physical expression of one or more genes. Get the Gizmo ready. Bull MD and the COMMITTEE ON GENETICS ABBREVIATIONS.
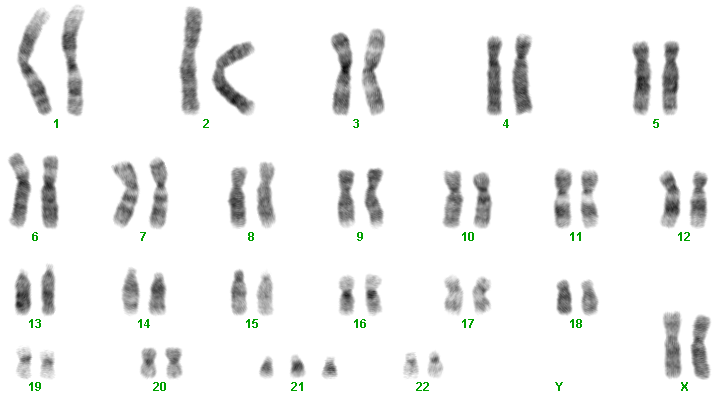
Journal of Intellectual Disability Research 42 Pt 4 293-300. Trisomy 21 Down syndrome for example occurs when there is an extra copy of chromosome 21 in one of the sex cells.
As a result recessive traits can be expressed.
Learn about Gregor Mendel his seminal experiments and the basic foundations of genetics in this videoPicture of Mendel by Hugo Iltis. Individuals with Down syndrome DS commonly possess unique neurocognitive and neurobehavioral profiles that emerge within specific developmental periods. Select the EXPERIMENTATION tab. WolfHirschhorn syndrome WHS is a chromosomal deletion syndrome resulting from a partial deletion on the short arm of chromosome 4 del4p163. Cardiofaciocutaneous syndrome is a disorder that affects many parts of the body particularly the heart cardio- facial features facio- and the skin and hair cutaneous. Bull MD and the COMMITTEE ON GENETICS ABBREVIATIONS. Most cases of Down syndrome result from trisomy 21 which means each cell in the body has three copies of chromosome 21 instead of the usual two copies. And long eyelashes extending down to the bridge of the nose long prominent philtrum with down-turned lip corners short and flattened nose hirsute forehead and cutis marmorata. How can offspring be created that have a specific phenotype and genotype.
Approximately 2 result from paternal uniparental disomy of 15q112-q13. WolfHirschhorn syndrome WHS is a chromosomal deletion syndrome resulting from a partial deletion on the short arm of chromosome 4 del4p163. The degree of intellectual disability varies from mild to moderate. A number sign is used with this entry because 4 known genetic mechanisms can cause Angelman syndrome AS. Features include a distinct craniofacial phenotype and intellectual disability Signs and symptoms. Less commonly Down syndrome occurs when part of chromosome 21 becomes attached translocated to another chromosome during the formation of reproductive cells eggs and sperm in a parent or very early in fetal development. In approximately 3 to 4 of persons with the Down syndrome phenotype the extra chromosomal material is the result of an unbalanced translocation between chromosome 21 and another acrocentric chromosome usually chromosome 14.








/down-syndrome-diagnosis-5b48ed9e46e0fb005b58a411.png)
















Post a Comment for "Phenotype Of Down Syndrome"