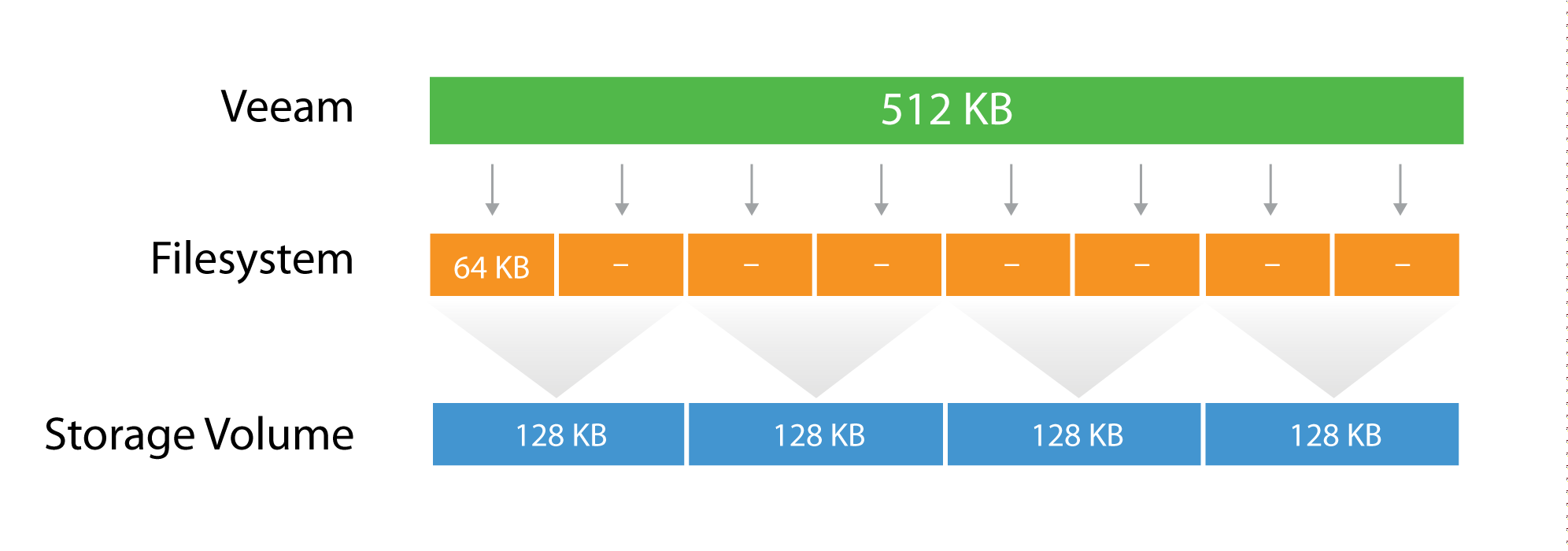
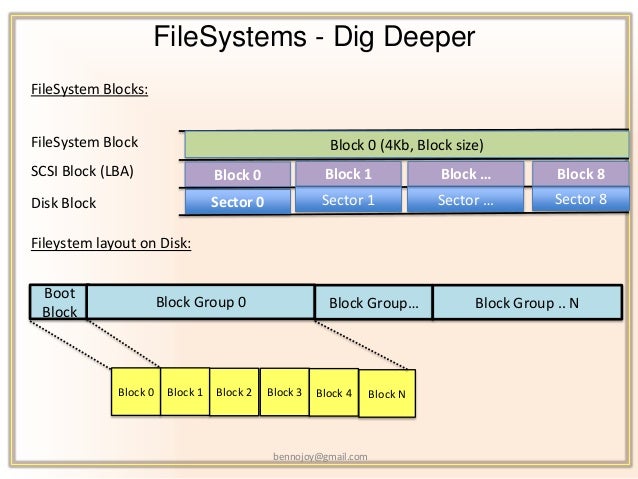
File System Block Size
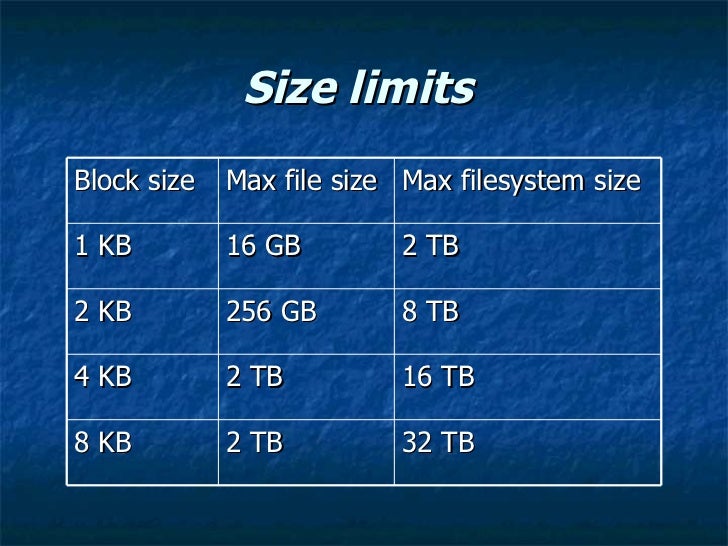
File system block size. Speaking of space management the file system is aware of every used and unused block on the partitions so itll be able to allocate space to new files or fetch the existing ones when requested. The default block size is 1024 bytes for file systems smaller than 1 TB and 8192 bytes for file systems 1 TB or larger. This Cluster is generally the smallest 4K and the large size is 32K 64K which is depending on the application.
Blockdev --getbsz devsda1 4096. Allocation may be on the basis of fixed-size blocks or variable-sized blocks. In this case the file allocation table contains a separate one-level index for each file.
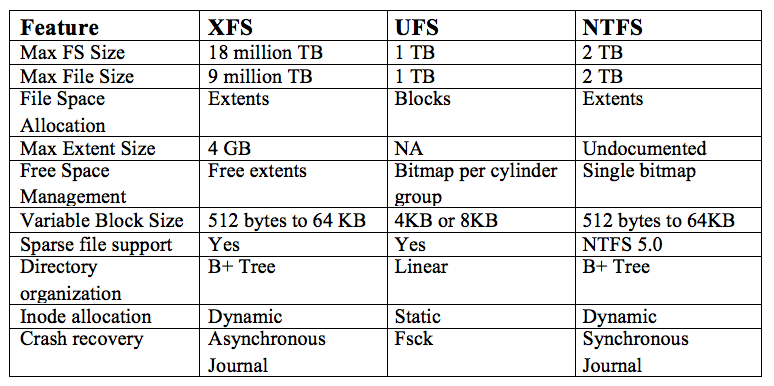
Allocation by blocks eliminates external fragmentation whereas allocation by variable-size blocks improves locality. Why change block size from 4K to 64K. The block size is the unit of work for the file system.
Microsoft Exchange server for example recommends the unit size be 64KB. The LFB size corresponds to 512 MB. In UNIX there will be du 1 which gives the file actual consumption on disk.
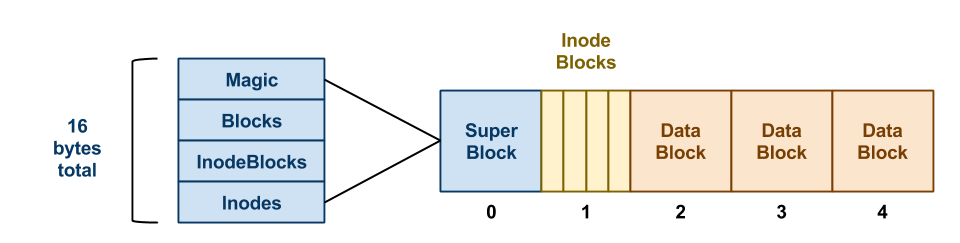
Super Block size of the file system block size of the file system empty or filled blocks of the file system size and allocation of inode tables. The default value of the logical block size is 4 KB. Every read and write is done in full multiples of the block size.
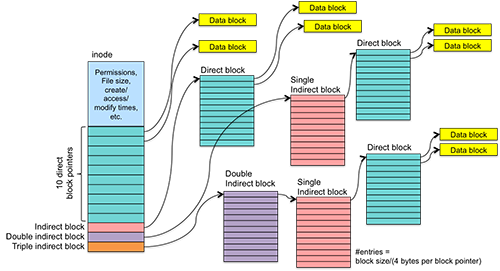
DATA STRUCTURE THE INODE The inode is the generic name that is used in many file systems to de- scribe the structure that holds the metadata for a given file such as its length permissions and the location of its constituent blocks. From the above example we can conclude that. For example the application of Oracle is generally used in 4K or 8K Block size and large file read-write can be used with 128K or even 256K.
The SFB can vary from 64 KB to 1 MB for future use cases but more often 1 MB is used. In general the file system block size will be 4K 8K 16K 32K 64K etc multiples of 4K.
A file in HDFS smaller than a single block does not occupy a full block size space of the underlying storage.
In this case the file allocation table contains a separate one-level index for each file. Suppose we have a file of size 612 MB and we are using the default block configuration 128 MBTherefore five blocks are created the first four blocks are 128 MB in size and the fifth block is 100 MB in size 1284100612. 1 Launch PowerShell Admin or Command Prompt Admin by using Win X. For example the application of Oracle is generally used in 4K or 8K Block size and large file read-write can be used with 128K or even 256K. A file in HDFS smaller than a single block does not occupy a full block size space of the underlying storage. The method getDefaultBlockSize has the following parameter. For example if there are many small files a 1 KB block size may save space. In this case the file allocation table contains a separate one-level index for each file. DATA STRUCTURE THE INODE The inode is the generic name that is used in many file systems to de- scribe the structure that holds the metadata for a given file such as its length permissions and the location of its constituent blocks.
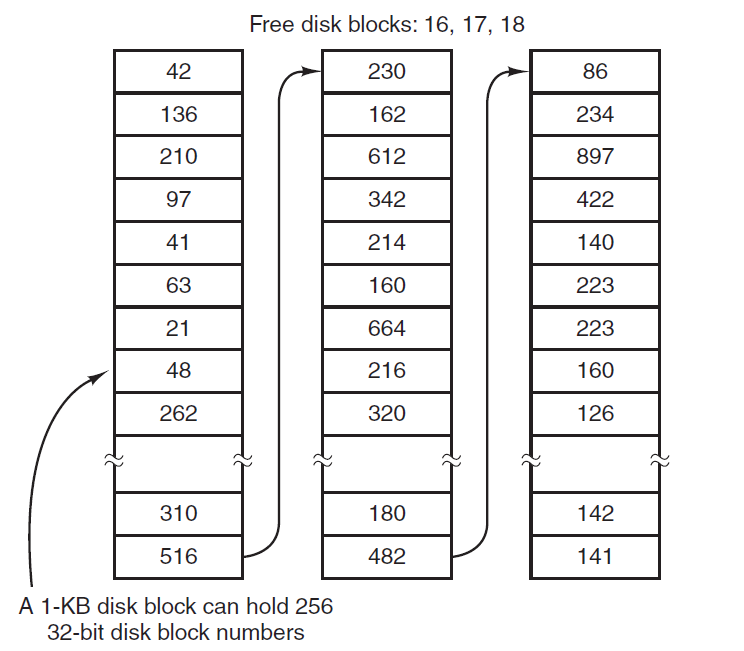
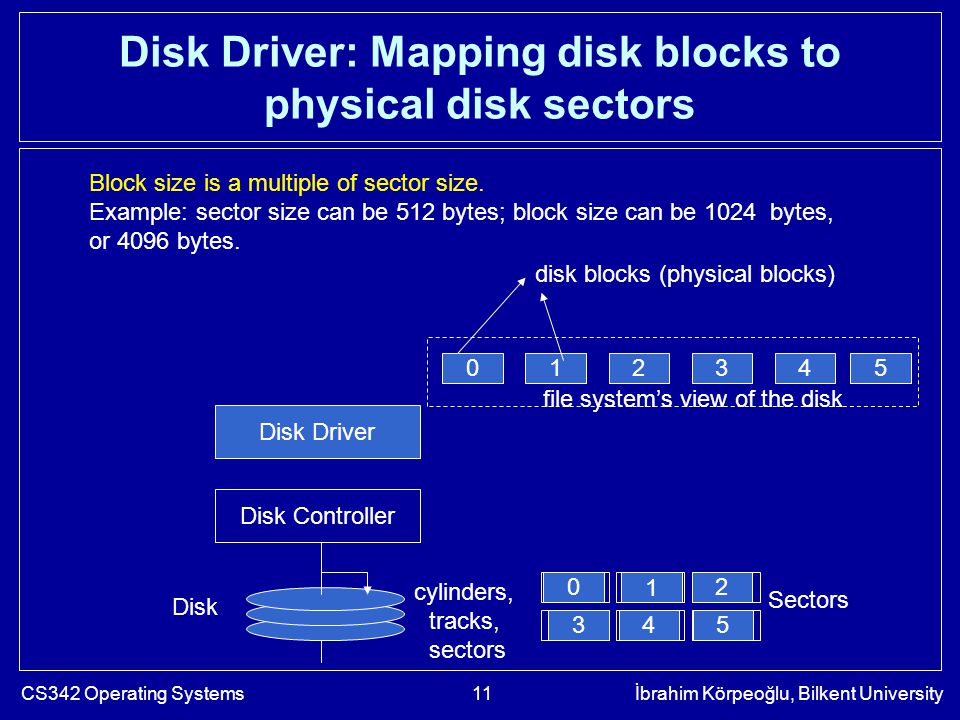
A block is a sequence of bit or Bytes with a fixed length ie 512 bytes 4kB 8kB 16kB 32kB etc. Speaking of space management the file system is aware of every used and unused block on the partitions so itll be able to allocate space to new files or fetch the existing ones when requested. This is the recommended block size for file systems larger than 100 MB. The file system is generally based on Cluster size sometimes called Block size to read and write data. Example The following code shows how to use Hadoop FileSystem getDefaultBlockSizePath f. 2 Use following command to show NTFS partition information. Limited by its Current Directory Structure CDS DOS does not support more than 32 directory levels except for DR DOS 331 - 60 or full pathnames longer than 66 bytes for FAT or 255 characters for LFNs.
































Post a Comment for "File System Block Size"